Class 12 Amines MCQ Questions are one of the best strategies to prepare for the CBSE Class 12 Board exam. If you want to complete a grasp concept or work on one’s score, there is no method except constant practice. Students can improve their speed and accuracy by doing more MCQ on Amines class 12 which will help them all through their board test.
Class 12 Amines MCQ Questions with Answers
Class 12 Chemistry MCQ with answers are given here to chapter the Amines. These MCQs are based on the latest CBSE board syllabus and relate to the latest Class 12 Chemistry syllabus. By Solving these Class 12 MCQ, you will be able to analyze all of the concepts quickly in the chapter and get ready for the Class 12 Annual exam.
Learn Class 12 Amines MCQ with answers pdf free download according to the latest CBSE and NCERT syllabus. Students should prepare for the examination by solving CBSE Amines Class 12 MCQ with answers given below.
Question 1. Aniline is reacted with bromine water and the resulting product is treated with an aqueous solution of sodium nitrite in presence of dilute hydrochloric acid. The compound so formed is converted into a tetrafluoroborate which is subsequently heated to dry. The final product is
(a) p-bromoaniline
(b) p-bromofluorobenzene
(c) 1, 3, 5-tribromobenzene
(d) 2, 4, 6-tribromofluorobenzene.
Answer
D
Question 2. Which of the following reactions is appropriate for converting acetamide to methanamine?
(a) Hoffmann hypobromamide reaction
(b) Stephen’s reaction
(c) Gabriel phthalimide synthesis
(d) Carbylamine reaction
Answer
A
Question 3. Which of the following will be most stable diazonium salt RN2+X –?
(a) CH3N2+X–
(b) C6H5N2+X–
(c) CH3CH2N2+X–
(d) C6H5CH2N2+X–
Answer
B
Question 4. Method by which aniline cannot be prepared is
(a) degradation of benzamide with bromine in alkaline solution
(b) reduction of nitrobenzene with H2/Pd in ethanol
(c) potassium salt of phthalimide treated with chlorobenzene followed by hydrolysis with aqueous NaOH solution
(d) hydrolysis of phenylisocyanide with acidic solution.
Answer
C
Question 5. The electrolytic reduction of nitrobenzene in strongly acidic medium produces
(a) azobenzene
(b) aniline
(c) p-aminophenol
(d) azoxybenzene.
Answer
C
Question 6. Nitrobenzene on reaction with conc. HNO3/H2SO4 at 80–100°C forms which one of the following products?
(a) 1, 4-Dinitrobenzene
(b) 1, 2, 4-Trinitrobenzene
(c) 1, 2-Dinitrobenzene
(d) 1, 3-Dinitrobenzene
Answer
D
Question 7. Electrolytic reduction of nitrobenzene in weakly acidic medium gives
(a) N-phenylhydroxylamine
(b) nitrosobenzene
(c) aniline
(d) p-hydroxyaniline.
Answer
C
Question 8. Acetamide is treated with the following reagents separately. Which one of these would yield methyl amine?
(a) NaOH-Br2
(b) Sodalime
(c) Hot conc.H2SO4
(d) PCl5
Answer
A
Question 9. Which one of the following on reduction with lithium aluminium hydride yields a secondary amine?
(a) Methyl isocyanide
(b) Acetamide
(c) Methyl cyanide
(d) Nitroethane
Answer
A
Question 10. In the chemical reaction,
CH3CH2NH2 + CHCI3 + 3KOH → A + B + 3H2O
The compounds A and B are respectively
(a) CH3CH2CONH2 and 3KCI
(b) C2H5NCand K2CO3
(c) C2H5NCand 3KCI
(d) C2H5CNand 3KCI
Answer
C
Question 11. Why do 2° and 3° amines fail to undergo the carbylamine test?
(a) They combine with chloroform to give a stable compound
(b) They react with alcoholic KOH
(c) The nitrogen atom of the amine group does not have the required number of hydrogen atoms
(d) All the given reasons are conect
Answer
B
Question 12. The correct sequence of reactions to convert p-nitrophenol into quinol involves
(a) reduction, diazotisation and hydrolysis
(b) hydrolysis, diazotisation and reduction
(c) hydrolysis, reduction and diazotisation
(d) diazotisation, reduction and hydrolysis
Answer
A
Question.13
![]() , D is
, D is
(a) CH3Br
(b) CH3CONH2
(c) CH3NH2
(d) CHBr3
Answer
C
Question 14. Consider the following reaction,
C6H5NO2 →Sn/HCI X →C6H5COCI Y + HCl What is Y ?
(a) Acetanilide
(b) Benzanilide
(c) Azobenzene
(d) Hydrazobenzene
Answer
B
Question 15. Which of the following is most basic in nature?
(a) NH3
(b) CH3NH2
(c) (CH3)2NH
(d) C6H5N(CH3)2
Answer
C
Question 16. C2H5NH2 →HNO2 A →PCI B →NH3 C.
Recognize the compound C from the following
(a) propanenitrile
(b) methylamine
(c) ethylamine
(d) acetamide
Answer
C
Question 17. Amino group is ortho,para-directing for aromatic electrophilic substitution. On nitration of aniline, a good amount of m-nitroaniline is obtained. This is due to
(a) in nitration mixture, ortho, para-activity of NH2 group is completely lost
(b) —NH2 becomes —NH+3, which is m-clirecting
(c) —NH2 becomes —NH+SO–4 , which is m-clirecting
(d) —NH2 becomes —NH–SO+2 , which ism-directing
Answer
A
Question 18. Choose the amide which on reduction with LiAIH4 yields a secondary amine
(a) ethanamide
(b) N-methylethanamide
(c) N, N-dimethylethanamide
(d) phenylmethanamide
(e) butanamide
Answer
B
Whoever needs to take the CBSE Class 12 Board Exam should look at this MCQ. To the Students who will show up in CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams, It is suggested to practice more and more questions. Aside from the sample paper you more likely had solved. These Class 12 Amines MCQ Questions with Answers are ready by the subject specialists themselves.
Question 19. Given the following sequence of reactions,
![]()
The major product C is
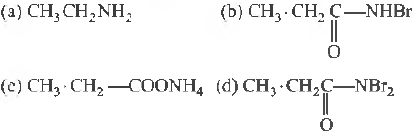
Answer
A
Question 20. Which of the following is strongest base?
(a) C6H5NH2
(b) p -NO2—C6H4NH2
(c) m-NO2—C6HNH2
(d) C6H5CH2NH2
Answer
D
Question 21. Intermediates formed during reaction of RCONH2 with Br2 and KOH are
(a) RCONHBr and RNCO
(b) RNHCOBr and RNCO
(c) RNH – Br and RCONHBr
(d) RCONBr2
Answer
A
Question 22. Name of method use to separate primary, secondary and tertiary amines is
(a) Hofmann method
(b) Lucas method
(c) Victor Meyer method
(d) Kolbe method
Answer
A
Question 23. Comparing basic strength of NH3 , CH3 NH2 and C6H5NH2 it may be concluded that
(a) basic strength remains unaffected
(b) basic strength of alkyl amines is lowest
(c) basic strength of aryl amines is lowest
(d) basic strength of NH3 is highest
Answer
C
Question 24. Indicate which nitrogen compound amongst the following would undergo Hoffmann reaction (i.e.,reaction with Br2 and strong KOH) to furnish the primary amine (R–NH2)?
(a) RCONHCH3
(b) RCOONH4
(c) RCONH2
(d) R – CO – NHOH
Answer
C
Question 25. The correct order of the basic strength of methyl substituted amines in aqueous solution is
(a) CH3NH2 > (CH3)2NH > (CH3)3N
(b) (CH3)2NH > CH3NH2 > (CH3)3N
(c) (CH3)3N > CH3NH2 > (CH3)2NH
(d) (CH3)3N > (CH3)2NH > CH3NH2
Answer
B
Question 26. Amides may be converted into amines by a reaction named after
(a) Hoffmann
(b) Claisen
(c) Perkin
(d) Kekule.
Answer
A
Question 27. Phenyl isocyanides are prepared by which of the following reaction?
(a) Reimer–Tiemann reaction
(b) Carbylamine reaction
(c) Rosenmund’s reaction
(d) Wurtz reaction
Answer
B
Question 28. The compound obtained by heating a mixture of ethylamine and chloroform with ethanolic potassium hydroxide (KOH) is
(a) an amide
(b) an amide and nitro compound
(c) an ethyl isocyanide
(d) an alkyl halide.
Answer
C
Question 29. Nitration of aniline in strong acidic medium also gives m-nitroaniline because
(a) inspite of substituents nitro group always goes to only m-position
(b) in electrophilic substitution reactions amino group is meta directive
(c) in absence of substituents nitro group alwaysgoes to m-position
(d) in acidic (strong) medium aniline is present as anilinium ion.
Answer
D
Question 30. The correct statement regarding the basicity of arylamines is
(a) arylamines are generally more basic than alkylamines because of aryl group
(b) arylamines are generally more basic than alkylamines, because the nitrogen atom in arylamines is sp-hybridised
(c) arylamines are generally less basic than alkylamines because the nitrogen lone-pair electrons are delocalised by interaction with the aromatic ring p-electron system
(d) arylamines are generally more basic than alkylamines because the nitrogen lone-pair electrons are not delocalised by interaction with the aromatic ring p-electron system.
Answer
C
Question 31. For carbylamine reaction, we need hot alcoholic KOH and
(a) any primary amine and chloroform
(b) chloroform and silver powder
(c) a primary amine and an alkyl halide
(d) a monoalkylamine and trichloromethane.
Answer
A
Question 32. Which product is formed, when acetonitrile is hydrolysed partially with cold concentrated HCl?
(a) Methyl cyanide
(b) Acetic anhydride
(c) Acetic acid
(d) Acetamide
Answer
D
Question 33. The action of nitrous acid on an aliphatic primary amine gives
(a) secondary amine
(b) nitro alkane
(c) alcohol
(d) alkyl nitrite.
Answer
C
Question 34. Which one of the following order is wrong, with respect to the property indicated?
(a) Benzoic acid > phenol > cyclohexanol (acid strength)
(b) Aniline > cyclohexylamine > benzamide (basic strength)
(c) Formic acid > acetic acid > propanoic acid (acid strength)
(d) Fluoroacetic acid > chloroacetic acid >bromoacetic acid (acid strength)
Answer
B
Question 35. Which of the following statements about primary amines is false?
(a) Alkyl amines are stronger bases than aryl amines.
(b) Alkyl amines react with nitrous acid to produce alcohols.
(c) Aryl amines react with nitrous acid to produce phenols.
(d) Alkyl amines are stronger bases than ammonia.
Answer
C
Question 36. Which of the following is more basic than aniline?
(a) Benzylamine
(b) Diphenylamine
(c) Triphenylamine
(d) p-Nitroaniline
Answer
A
Question 37. On hydrolysis of a “compound”, two compounds are obtained. One of which on treatment with sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid gives a product which does not respond to iodoform test. The second one reduces Tollens’ reagent and Fehling’s solution. The “compound” is
(a) CH3CH2CH2NC
(b) CH3CH2CH2CN
(c) CH3CH2CH2ON O
(d) CH3CH2CH2CON(CH3)2
Answer
A

You can easily get good marks If you study with the help of Amines Class 12 MCQ. We trust that information provided is useful for you. NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 12 Amines PDF Free Download would without a doubt create positive results.
We hope the information shared above in regards to MCQ on Amines Class 12 with Answers has been helpful to you. if you have any questions regarding CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Solutions MCQs Pdf, write a comment below and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
How many MCQ questions are there in Cass 12 chapter 13 Chemistry?
In Class 12 chapter 13 Chemistry, we have provided 37 Important MCQ Questions, But in the future, we will add more MCQs so that you can get good marks in the Class 12 exam.
Can we score good marks in Class 12 Chemistry with the help of Amines MCQ Questions?
Yes, MCQ Question is one of the best strategies to make your preparation better for the CBSE Board Exam. It also helps to know the student’s basic understanding of each chapter. So, You can score good marks in the Class 12 Chemistry exam.

