Class 12 Aldehyde Ketone and Carboxylic Acid MCQ Questions are one of the best strategies to prepare for the CBSE Class 12 Board exam. If you want to complete a grasp concept or work on one’s score, there is no method except constant practice. Students can improve their speed and accuracy by doing more MCQ on Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic acids class 12 which will help them all through their board test.
Class 12 Aldehyde Ketone and Carboxylic Acid MCQ Questions with Answers
Class 12 Chemistry MCQ with answers are given here to chapter the Aldehyde Ketone and Carboxylic Acid . These MCQs are based on the latest CBSE board syllabus and relate to the latest Class 12 Chemistry syllabus. By Solving these Class 12 MCQ, you will be able to analyze all of the concepts quickly in the chapter and get ready for the Class 12 Annual exam.
Learn Class 12 Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ with answers pdf free download according to the latest CBSE and NCERT syllabus. Students should prepare for the examination by solving CBSE Class 12 Aldehyde Ketone and Carboxylic Acid MCQ with answers given below.
Question 1. Ketones [RCOR1] where R = R1 = alkyl group. It can be obtained in one step by
(a) oxidation of tertiary alcohol
(b) reaction of acid halide with alcohols
(c) hydrolysis of esters
(d) oxidation of primary alcohol.
Answer
A
Question 2.Which one of the following can be oxidised to the corresponding carbonyl compound?
(a) 2-Hydroxypropan
(b) ortho-Nitrophenol
(c) Phenol
(d) 2-Methyl-2-hydroxypropane
Answer
A
Question 3. In the reaction, CH3CN + 2H → HCl Ether → X→ Boiling H2OY; the term Y is
(a) acetaldehyde
(b) ethanamine
(c) acetone
(d) dimethylamine.
Answer
A
Question 4. Which of the following reagents would distinguish cis-cyclopenta-1,2-diol from the trans-isomer?
(a) MnO2
(b) Aluminium isopropoxide
(c) Acetone
(d) Ozone
Answer
C
Question 5. The oxidation of toluene to benzaldehyde by chromyl chloride is called
(a) Etard reaction
(b) Riemer–Tiemann reaction
(c) Wurtz reaction
(d) Cannizzaro’s reaction.
Answer
A
Question 6. Reaction between benzaldehyde and acetophenone in presence of dilute NaOH is known as
(a) Aldol condensation
(b) Cannizzaro’s reaction
(c) Cross Cannizzaro’s reaction
(d) Cross Aldol condensation.
Answer
D
Question 7. CH3CHO and C6H5CH2CHO can be distinguished chemically by
(a) Benedict’s test
(b) iodoform test
(c) Tollens’ reagent test
(d) Fehling’s solution test.
Answer
B
Question 8. Consider the reaction : RCHO + NH2NH2 → RCH=N — NH2 What sort of reaction is it?
(a) Electrophilic addition-elimination reaction
(b) Free radical addition-elimination reaction
(c) Electrophilic substitution-elimination reaction
(d) Nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction
Answer
D
Question 9. Which of the following compounds will give a myellow precipitate with iodine and alkali?
(a) Acetophenone
(b) Methyl acetate
(c) Acetamide
(d) 2-Hydroxypropane
Answer
A,D
Question 10. The correct statement regarding a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alphacarbon, is
(a) a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon rapidly equilibrates with its corresponding enol and this process is known as carbonylation
(b) a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon rapidly equilibrates with its corresponding enol and this process is known as keto-enol tautomerism
(c) a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon never equilibrates with its corresponding enol
(d) a carbonyl compound with a hydrogen atom on its alpha-carbon rapidly equilibrates with its corresponding enol and this process is known as aldehyde-ketone equilibration
Answer
B
Question 11. The product formed by the reaction of an aldehyde with a primary amine is
(a) carboxylic acid
(b) aromatic acid
(c) Schiff ’s base
(d) ketone.
Answer
C
Question 12. Reaction of a carbonyl compound with one of the following reagents involves nucleophilic addition followed by elimination of water. The reagent is
(a) hydrazine in presence of feebly acidic solution
(b) hydrocyanic acid
(c) sodium hydrogen sulphite
(d) a Grignard reagent.
Answer
A
Question 13. A strong base can abstract an a-hydrogen from
(a) ketone
(b) alkane
(c) alkene
(d) amine.
Answer
A
Question 14. Reduction of aldehydes and ketones into hydrocarbons using zinc amalgam and conc. HCl is called
(a) Cope reduction
(b) Dow reduction
(c) Wolff–Kishner reduction
(d) Clemmensen reduction.
Answer
D
Question 15. Clemmensen reduction of a ketone is carried out in the presence of which of the following?
(a) Glycol with KOH
(b) Zn-Hg with HCl
(c) LiAlH4
(d) H2 and Pt as catalyst
Answer
B
Question 16. Which of the following reactions will not result in the formation of carbon-carbon bonds?
(a) Reimer–Tiemann reaction
(b) Cannizzaro reaction
(c) Wurtz reaction
(d) Friedel–Crafts acylation
Answer
B
Question 17. Which of the following can be used to differentiate between aldehyde and ketone?
(a) Ammoniacal AgNO3
(b) Ammoniacal AgNO3 in the presence oftartarate ion
(c) I2 in the presence of base
(d) Ammoniacal AgNO3 in the presence of citrate ion
Answer
A
Question 18. A compound X undergoes reduction with LiAIH4 to yield Y . When vapours of Yare passed over freshly reduced copper at 300° C, X is formed. What is Y?
(a) CH3COCH3
(b) CH3CHO
(c) CH3CH2OH
(d) CH3OCH3
Answer
C
Question 19. The product formed in the aldol condensation of acetaldehyde is
(a) CH3CH2CH(OH)CHO
(b) CH3CH(OH)CH2CHO
(c) CH3CH(OH)COCH3
(d) CH3CH2CH2CHO
Answer
B
Question 20. The product formed in aldol condensation is A
(a) a beta-hydroxy aldehyde or a beta-hydroxy ketone
(b) an alpha-hydroxy aldehyde or ketone
(c) an alpha, beta unsaturated ester
(d) a beta-hydroxy acid.
Answer
A
Question 21. Aldo! condensation is given by
(a) trimethyl acetaldehyde
(b) acetaldehyde
(c) benzaldehyde
(d) formaldehyde
Answer
B
Question 22. Which of the following will form two isomers with semi carbazide ?
(a) Benzaldehyde
(b) Acetone
(c) Benzoquinone
(d) Benzophenone
Answer
A
Question 23. In the reaction
CH3COOH →LiAIH4 A →PCl5 B →Ale.KOH C, the product C is
(a) acetaldehyde
(b) acetylene
(c) ethylene
(d) acetyl chloride
Answer
C
Question 24. The reaction of an organic compound with ammonia followed by nitration of the product gives a powerful explosive, called RDX. The organic compound is
(a) phenol
(b) toluene
(c) glycerine
(d) formaldehyde
Answer
D
Question 25. Which of the following does not give Fehling solution test?
(a) Acetone
(b) Propanal
(c) Ethanal
(d) Butanal
Answer
A
Question 26. Which of the product is formed when acetone is reacted with barium hydroxide solution?

Answer
A
Question 27. The correct increasing order of the acid strength ofbenzoic acid (I), 4-nitrobenzoic acid (II), 3, 4-dinitrobenzoic acid (III) and 4methoxybenzoic acid (IV) is
(a) I < II < III < IV
(b) II < I < IV < III
(c) IV < I < II < III
(d) IV < II < I < III
(e) I < IV < II < III
Answer
C
Question 28. Identify Din the following reaction

(a) HOOC—CH2—COOH
(b) OHC—CH2—COOH
(c) OHC—CH2—CHO
(d) HO—CH=CH—COOH
Answer
B
Question 29. A liquid was mixed with ethanol and a drop of concentrated H2SO4 was added. A compound with a fruity smell was formed. The liquid was
(a) CH3OH
(b) HCHO
(c) CH3COCH3
(d) CH3COOC2H5
Answer
D
Question 30. 2-pentanone and 3-petanone can be distinguished by
(a) Cannizzaro’s reaction
(c) Iodoform reaction reduction
(b) Aldo! condensation
(d) Clemmensen’s
Answer
C
Question 31. Sodium phenoxide when heated with CO2 under pressure at 125°C yields a product which on acetylation producesC.
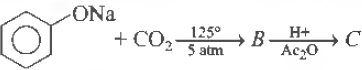

Answer
A
Question 32. Vinegar is dilute aqueous solution of
(a) ethanoic acid
(b) benzoic acid
(c) citric acid
(d) oxalic acid
Answer
A
Question 33. Which one of the following acid does not have a carboxylic group?
(a) Methanoic acid
(b) Ethanoic acid
(c) Propanoic acid
(d) Picric acid
Answer
D
Whoever needs to take the CBSE Class 12 Board Exam should look at this MCQ. To the Students who will show up in CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams, It is suggested to practice more and more questions. Aside from the sample paper you more likely had solved. These Class 12 Aldehyde Ketone and Carboxylic Acid MCQ Questions with Answers are ready by the subject specialists themselves.
Question 34. What product is formed when cyclohexanone is oxidised?
(a) HOOC. (CH2)4 · COOH
(b) CH3CH2COOH
(c) CH3(CH2)4COOH
(d) None of the above
Answer
A
Question 35. Identify the method by which Me3CCO2H can be prepared.
(a) Treating 1 mole of MeCO Me with 2 moles of MeMgI
(b) Treating 1 mole of MeCO2 Me with 3 moles of MeMgI
(c) Treating 1 mole of MeCHO with 3 moles of MeMgI
(d) Treating 1 mole of dry ice with 1 mole of Me3CMgI
Answer
D
Question. 36
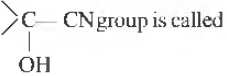
(a) hydroxy nitrite
(c) cyanohydrin
(b) hydroxy cyanide
(d) hydroxy isocyanide
Answer
C
Question 37. The compound that undergoes decarboxyliation most readily under mild condition is
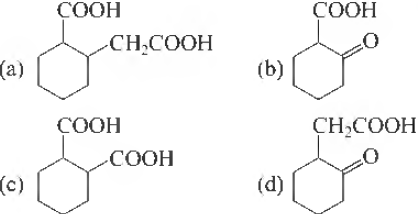
Answer
B
Question 38. Among the following compounds, the one(s) that gives (give) effervescence with aqueous NaHCO3 solution is (are)
(CH3CO)2 OCH3COOHPhOHCH3COCHO
I II III IV
(a) I and II
(b) I and III
(c) Only II
(d) 1 and IV
Answer
A
Question 39. Which acid is present in vinegar?
(a) Formic acid
(b) Acetic acid
(c) Butyric acid
(d) Tartaric acid
Answer
B
Question 40. Which one of the following is an Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction?
(a)![]()

(d)![]()
Answer
B
Question 41. The strongest acid amongst the following compounds is
(a) CH3COOH
(b) HCOOH
(c) CH3CH2CH(Cl)CO2H
(d) ClCH2CH2CH2COOH
Answer
C
Question 42. Benzaldehyde on refluxing with aqueous alcoholic KCN produce
(a) cyanobenzene
(b) cyanohydrin
(c) benzoyl cyanide
(d) benzoin
Answer
D
Question 43. Which of the following is incorrect?
(a) FeCl3 is used in detection of phenol.
(b) Fehling solution is used in detection of glucose.
(c) Tollens’ reagent is used in detection of unsaturation.
(d) NaHSO3 is used in detection of carbonyl compound.
Answer
C
Question 44. Polarisation in acrolein can be described as
(a) +δCH2=CH — +δCHO
(b) -δCH2= CH — +δCHO
(c) -δCH2= CH — CHO+δ
(d) +δCH= CH — CHO-δ
Answer
D
Question 45. A carbonyl compound reacts with hydrogen cyanide to form cyanohydrin which on hydrolysis forms a racemic mixture of a-hydroxy acid. The carbonyl compound is
(a) formaldehyde
(b) acetaldehyde
(c) acetone
(d) diethyl ketone.
Answer
B
Question 46. In this reaction : CH3CHO + HCN → CH3CH(OH)CN →HOH CH3CH(OH)COOH an asymmetric centre is generated. The acid obtained would be
(a) D-isome
(b) L-isomer
(c) 50% D + 50% L-isomer
(d) 20% D + 80% L-isomer.
Answer
C
Question 47. Iodoform test is not given by
(a) ethanal
(b) ethanol
(c) 2-pentanone
(d) 3-pentanone.
Answer
D
Question 48. Phenylmethanol can be prepared by reducing the benzaldehyde with
(a) CH3Br and Na
(b) CH3I and Mg
(c) CH3Br
(d) Zn and HCl.
Question 49. The oxidation of toluene with CrO3 in the presence of (CH3CO)2O gives a product A, which on treatment with aqueous NaOH produces
(a) C6H5COONa
(b) 2, 4-diacetyl toluene
(c) C6H5CHO
(d) (C6H5CO)2O
Answer
A
Question 50. First product of the reaction between RCHO and NH2NH2 is
(a) RCH NNH2
(b) RCH NH
(c) RCH2NH2
(d) RCON3
Answer
A
Question 51. An ester (A) with molecular formula, C9H10O2 was treated with excess of CH3MgBr and the complex so formed, was treated with H2SO4 to give an olefin (B). Ozonolysis of (B) ave a ketone with molecular formula C8H8O which shows +ve iodoform test. The structure of (A) is
(a) H3CCH2COC6H5
(b) C2H5COOC6H5
(c) C6H5COOC2H5
(d) p-H3CO – C6H4 – COCH3
Answer
C
Question 52. Which of the following compounds will undergo self aldol condensation in the presence of cold dilute alkali?
(a) CH C — CHO
(b) CH2 CHCHO
(c) C6H5CHO
(d) CH3CH2CHO
Answer
D
Question 53. Which of the following compounds will give positive test with Tollens’ reagent?
(a) Acetic acid
(b) Acetone
(c) Acetamide
(d) Acetaldehyde
Answer
D
Question 54. (CH3)2C= CHCOCH3 can be oxidised to (CH3)2C=CHCOOH by
(a) chromic acid
(b) NaOI
(c) Cu at 300°C
(d) KMnO4
Answer
B
Question 55. When aniline reacts with oil of bitter almonds (C6H5CHO) condensation takes place and benzal derivative is formed. This is known as
(a) Schiff ’s base
(b) Benedict’s reagent
(c) Millon’s base
(d) Schiff ’s reagent.
Answer
A
Question 56. Compound A has a molecular formula C2Cl3OH. It reduces Fehling’s solution and on oxidation, it gives a monocarboxylic acid B. If A is obtained by the action of chlorine on ethyl lcohol, then compound A is
(a) methyl chloride
(b) monochloroacetic acid
(c) chloral
(d) chloroform.
Answer
C
Question 57. In which of the following, the number of carbon atoms does not remain same when carboxylic acid is obtained by oxidation?
(a) CH3COCH3
(b) CCl3CH2CHO
(c) CH3CH2CH2OH
(d) CH3CH2CHO
Answer
A
Question 58. The reagent which can be used to distinguish acetophenone from benzophenone is
(a) 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine
(b) aqueous solution of NaHSO3
(c) Benedict reagent
(d) I2 and NaOH.
Answer
D
Question 59. If formaldehyde and KOH are heated, then we get
(a) methane
(b) methyl alcohol
(c) ethyl formate
(d) acetylene.
Answer
B
Question 60. Acetaldehyde reacts with
(a) electrophiles only
(b) nucleophiles only
(c) free radicals only
(d) both electrophiles and nucleophiles.
Answer
B
Question 61. Which of the following compounds gives benzoic acid on hydrolysis?
(a) Chlorobenzene
(b) Benzoyl chloride
(c) Chlorophenol
(d) Chlorotoluene
Answer
B
Question 62. The correct order of decreasing acid strength of trichloroacetic acid (A), trifluoroacetic acid (B), acetic acid (C) and formic acid (D) is
(a) B > A > D > C
(b) B > D > C > A
(c) A > B > C > D
(d) A > C > B > D
Answer
A
Question 63. An organic compound A on treatment with NH3 gives B, which on heating gives C. C when treated with Br2 in the presence of KOH produces ethyl amine. Compound A is
(a) CH3COOH
(b) CH3CH2CH2COOH
(c) CH3— CHCOOH ι
CH3
(d) CH3CH2COOH
Answer
D
Question 64. Which of the following represents the correct order of the acidity in the given compounds?
(a) FCH2COOH > CH3COOH > BrCH2COOH > ClCH2COOH
(b) BrCH2COOH > ClCH2COOH > FCH2COOH > CH3COOH
(c) FCH2COOH > ClCH2COOH > BrCH2COOH > CH3COOH
(d) CH3COOH > BrCH2COOH > ClCH2COOH > FCH2COOH
Answer
C
Question 65. Carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular mass. It is due to their
(a) formation of intramolecular H-bonding
(b) formation of carboxylate ion
(c) more extensive association of carboxylic acid via van der Waals’ forces of attraction
(d) formation of intermolecular H-bonding.
Answer
D

You can easily get good marks If you study with the help of Aldehyde Ketone and Carboxylic Acid Class 12 MCQ. We trust that information provided is useful for you. NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 12 Aldehyde Ketone and Carboxylic Acid PDF Free Download would without a doubt create positive results.
We hope the information shared above in regards to MCQ on Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic acids with Answers has been helpful to you. if you have any questions regarding CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Solutions MCQs Pdf, write a comment below and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
How many MCQ questions are there in Cass 12 chapter 12 Chemistry?
In Class 12 chapter 12 Chemistry, we have provided 65 Important MCQ Questions, But in the future, we will add more MCQs so that you can get good marks in the Class 12 exam.
Can we score good marks in Class 12 Chemistry with the help of Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic acids MCQ Questions?
Yes, MCQ Question is one of the best strategies to make your preparation better for the CBSE Board Exam. It also helps to know the student’s basic understanding of each chapter. So, You can score good marks in the Class 12 Chemistry exam.

